Calculators + Utilities: Difference between revisions
(→Material Parameters: added Lesker links) |
m (→CAD Files & Templates: indent figure) |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Fabrication Processes & Converters== |
==Fabrication Processes & Converters== |
||
*[https://trello.com/b/Oxs8nMlt/example-fabrication-jobs-board Example Fab Job tracking on Trello] |
|||
**Includes Example Travelers/Process Followers ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manufacturing_execution_system MEC], process documentation+tracking) |
|||
**Includes Example [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Design_of_experiments DOE] spreadsheets - how to organize a process development experiment according to the scientific method. |
|||
*[https://cleanroom.byu.edu/oxidetimecalc/ Thermal Oxide Calculator (BYU)] |
*[https://cleanroom.byu.edu/oxidetimecalc/ Thermal Oxide Calculator (BYU)] |
||
| Line 52: | Line 56: | ||
**You can share an interactive 3D render of your [[Atomic Force Microscope (Bruker ICON)|AFM]] or [[Optical Profilometer - White-Light/Phase-Shift Interference (Filmetrics Profilm3D)|Profilm3D]] scans with this tool. |
**You can share an interactive 3D render of your [[Atomic Force Microscope (Bruker ICON)|AFM]] or [[Optical Profilometer - White-Light/Phase-Shift Interference (Filmetrics Profilm3D)|Profilm3D]] scans with this tool. |
||
**[https://www.profilmonline.com/s/cjezAEur8mC2 Example AFM Scan], taken with NanoFab equipment, shared online for interactive analysis (slice, flatten etc.). |
**[https://www.profilmonline.com/s/cjezAEur8mC2 Example AFM Scan], taken with NanoFab equipment, shared online for interactive analysis (slice, flatten etc.). |
||
== CAD Layout and Mask Design == |
|||
===CAD Layout Programs=== |
===CAD Layout Programs=== |
||
| Line 61: | Line 67: | ||
*UCSB's ECE dept. provides an '''academic''' license for this software (no industrial users!), email [mailto:help@ece.ucsb.edu help@ece.ucsb.edu] to obtain the software. |
*UCSB's ECE dept. provides an '''academic''' license for this software (no industrial users!), email [mailto:help@ece.ucsb.edu help@ece.ucsb.edu] to obtain the software. |
||
*Windows only. |
*Windows only. |
||
*See [https://wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/wiki/Images/uploads/2018/LEdit_GettingStarted_CherryGupta.pdf this L-Edit Tutorial] for a good starter guide. Written by [https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=qKzZc7AAAAAJ&hl=en Cherry Gupta], courtesy of [https://me.ucsb.edu/people/sumita-pennathur Prof. Sumita Pennathur]. |
*See [https://wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/wiki/Images/uploads/2018/LEdit_GettingStarted_CherryGupta.pdf this '''L-Edit Tutorial'''] for a good starter guide. Written by [https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=qKzZc7AAAAAJ&hl=en Cherry Gupta], courtesy of [https://me.ucsb.edu/people/sumita-pennathur Prof. Sumita Pennathur]. |
||
====[https://www.klayout.de KLayout]==== |
====[https://www.klayout.de KLayout]==== |
||
A free, open-source, and fast/simple CAD tool for mask/reticle layout. |
A free, open-source, and fast/simple CAD tool for mask/reticle layout. Also has powerful functions, DRC, scriptiable and can handle very large files (GB's) efficiently. |
||
Download at [https://www.klayout.de/ klayout.de]. |
|||
*Available on Windows, Mac or *Nix. |
*Available on Windows, Mac or *Nix. |
||
*Easily scriptable with Python or Ruby, with decent tutorials. |
|||
*Fast viewing of layer overlay, overlay multiple files, cell hierarchy, large (>1GB) files etc. |
*Fast viewing of layer overlay, overlay multiple files, cell hierarchy, large (>1GB) files etc. |
||
*Supports the same core functionality as L-Edit - hierarchical Cell Instances, arrays, programmable Cells (PCells) etc. |
*Supports the same core functionality as L-Edit - hierarchical Cell Instances, arrays, programmable Cells (PCells) etc. |
||
*Easily scriptable with Python or Ruby, with decent tutorials. |
|||
*Please visit the [[KLayout Design Tips]] page for important info on making "valid" CAD files, along with setting up the program for efficient use. |
|||
*[[KLayout Design Tips|<u>KLayout Design Tips</u>]]: important info on making "valid" CAD files, and setting up the program for efficient use. |
|||
*''Before'' starting your design, set the '''''Layout Properties > Database Unit''''' to something small eg. the default of 0.001 µm (1nm) is usually fine. Don't change this after drawing - everything will be scaled accordingly. |
|||
*Univ. of Waterloo QNFCF has produced some good [https://www.youtube.com/@qnfcf6093/videos '''''video tutorials on KLayout, here''''']. |
|||
*Turn on the display of the Origin (0,0) in '''''Preferences > Display > Background > Axis''''' = change from the default "invisible", eg. "'''''Lines with Ticks'''''". |
|||
*How to draw circles: You have to draw a square, and then apply the function '''''Edit > Selection > Convert to PCell'' > Basic.CIRCLE'''. Sometimes these P-Cells don't convert properly at the photomask vendor, so make sure to run '''''Edit > Selection > Convert to Static Cell''''' before taping out to the vendor. |
|||
**Another way is to convert a square to a polygon directly with '''''Edit>Selection>Round Corners''''' function with '''''Outer Corner Radius''''' = the desired circle radius (radius is not changeable afterards in this method, but computation may be faster for a large number of objects). |
|||
**Klayout doesn't natively support circles because the GDS file format does not have a "circle" primitive built-in, so instead it creates a polygon. Make sure you include enough polygon points, eg. 32. See the [https://www.klayout.de/forum/discussion/142/making-circles forum help pages] on this for more info. |
|||
==== [https://layouteditor.com/ LayoutEditor] ==== |
|||
====CAD Design Tips==== |
|||
It is highly recommended that you understand and use the concept of "Cells" in your design. This circumvents many problems with enormous file sizes (due to huge numbers of identical polygons), and if used properly, helps tremendously with programming the Stepper lithography machines. Links to documentation below: |
|||
* Free editor for GDS, OASIS, DXF etc. available on Windows, MacOS, Linux. |
|||
*Create a new cell, and instancing that cell: [https://www.klayout.de/doc-qt4/manual/create_instance.html KLayout Docs : Creating a Cell instance] |
|||
* Scriptable with Python, Ruby, C++ |
|||
====AutoCAD==== |
|||
Many photomask vendors can accept AutoCAD DWG files, but these can only be opened in AutoCAD (not KLayout or other layout programs). Although AutoCAD can produce a cross-compatible DXF file, we see many design/conversion issues with these files. This is because many shapes and line-types (Curves and Line/polyline/LWLine for example) used in AutoCAD don't convert as expected into the polygons needed for printing. Also the DXF file format itself often creates problems, such as incorrect scaling or badly-filled/unclosed polygons. |
|||
===CAD Design Tips=== |
|||
=====''Cells and Instancing''===== |
|||
All major chip layout programs support "Cells" and similar structures for hierarchical layout. It is highly recommended that you understand and use the concept of "Cells" in your design. This circumvents many problems with enormous file sizes (due to huge numbers of identical polygons), and if used properly, helps tremendously with programming the Stepper lithography machines. Links to documentation below: |
|||
*Create a new cell, and instancing that cell: [https://www.klayout.de/doc/manual/create_instance.html KLayout Docs : Creating a Cell instance] |
|||
*Viewing only some levels of the heirachy, to prevent drawing all objects: [https://www.klayout.de/doc/manual/hier.html KLayout Docs: Viewing Cell Heirarchy] |
*Viewing only some levels of the heirachy, to prevent drawing all objects: [https://www.klayout.de/doc/manual/hier.html KLayout Docs: Viewing Cell Heirarchy] |
||
=====''File Types''===== |
|||
OASIS files tend to be much smaller than GDS files, and they also save the Layer Names (not just number). Alternatively, in KLayout the function '''File > Save Session''' will save the entire view including layer styles and window/zoom locations will be saved. You can share this file, as the entire design file is embedded within it, but it may not be as robust between KLayout versions. |
OASIS files tend to be much smaller than GDS files, and they also save the Layer Names (not just number). Alternatively, in KLayout the function '''File > Save Session''' will save the entire view including layer styles and window/zoom locations will be saved. You can share this file, as the entire design file is embedded within it, but it may not be as robust between KLayout versions. |
||
DXF Files can often cause problems because the format varies widely depending on the program they are exported from. For example, DXF can lose the "scaling" causing polygons to be 1000x larger than expected, or unexpectedly cause some shares to get filled in. |
|||
=====[[KLayout Design Tips|''KLayout Design Tips'']]===== |
|||
See the above page for important info on making "valid" CAD files, and setting up KLayout for efficient use. |
|||
=====''Handling very large files''===== |
=====''Handling very large files''===== |
||
| Line 93: | Line 113: | ||
#Photomask vendors are able to take multiple files and insert them into the final reticle – you just need to provide a clear schematic showing the exact insertion coordinates for each file (with respect to the origin of each file). They can also do some boolean operations (for a fee). |
#Photomask vendors are able to take multiple files and insert them into the final reticle – you just need to provide a clear schematic showing the exact insertion coordinates for each file (with respect to the origin of each file). They can also do some boolean operations (for a fee). |
||
===Example CAD File=== |
|||
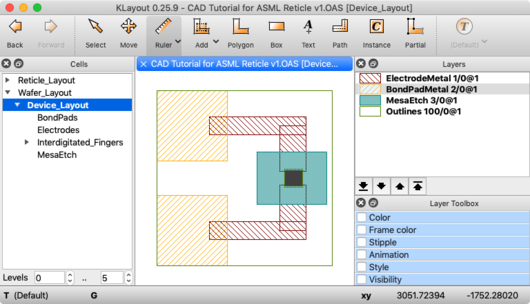
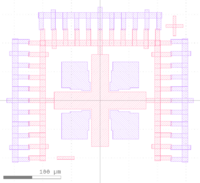
Here is an example CAD file, showing the use of Layers and Cells, designed in KLayout. The device is fictional, for illustrative purposes only. |
Here is an example CAD file, showing the use of Layers and Cells, designed in KLayout. The device is fictional, for illustrative purposes only. |
||
*[//wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/w/images/a/ae/CAD_Tutorial_for_ASML_Reticle_v1.OAS |
*[//wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/w/images/a/ae/CAD_Tutorial_for_ASML_Reticle_v1.OAS CAD_Tutorial_for_Reticle_v1.OAS] , or [[Media:CAD Tutorial for ASML Reticle v1 GDS.gds|GDS version]] (''Demis D. John'') |
||
*Cell "'''Device_Layout'''" shows a single device, with each ''Layer'' overlaid as it would be in a fabricated device. Each Layer (eg. a "process step" such as Mesa etch, Pad Metal etc.) is placed into it's own Cell. |
*Cell "'''Device_Layout'''" shows a single device, with each ''Layer'' overlaid as it would be in a fabricated device. Each Layer (eg. a "process step" such as Mesa etch, Pad Metal etc.) is placed into it's own Cell. |
||
| Line 104: | Line 124: | ||
**One way this can be accomplished is by selecting the objects/polygons you want to make into a new Cell, then use the function '''Edit >''' '''Selection > Make Cell''', and ''uncheck'' the "''Put Origin at...''" checkbox, so the new Cell maintains the same origin as the original view. |
**One way this can be accomplished is by selecting the objects/polygons you want to make into a new Cell, then use the function '''Edit >''' '''Selection > Make Cell''', and ''uncheck'' the "''Put Origin at...''" checkbox, so the new Cell maintains the same origin as the original view. |
||
*The Cell "'''Reticle_Layout'''" can be exported by itself (right-click the Cell name), for sending to the photomask manufacturer. |
*The Cell "'''Reticle_Layout'''" can be exported by itself (right-click the Cell name), for sending to the photomask manufacturer. |
||
**[//wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/w/images/3/34/DEMISJAN2020_-_Reticle_Layout_v1.GDS Here is |
**[//wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/w/images/3/34/DEMISJAN2020_-_Reticle_Layout_v1.GDS Here is an example GDS file (download)] for submission to the photomask manufacturer, with all objects moved to a single Layer. |
||
*See the [[ |
*See the [[Stepper Mask-Making Guidelines (Generic)|Stepper Mask Making Guidelines page]] for an example of how to program this Reticle into an ASML Stepper job. |
||
=== |
===CAD Files & Templates=== |
||
====General CAD files for Lithography==== |
|||
*[[Media:Vented font DDJ.gds|Vented Font (GDS)]] - a font good for liftoff (no enclosed holes). (Designed by [[Demis D. John]]) |
|||
**See [https://www.klayout.de/forum/discussion/comment/6919/#Comment_6919 this comment] for instructions on installing the font into KLayout.[[File:Vented font screnshot.jpg|alt=Screenshot of Vented_font_DDJ.gds|none|thumb|200x200px|Vented font schematic.]] |
|||
*[[Media:Vernier Template.gds|Alignment/Registration Vernier Scales (GDS)]] - used to measure the misalignment between different layers (step=0.1um). (Designed by [[Demis D. John]]) |
|||
**[http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee143/fa10/lab/vernier.pdf How to use a Vernier Scale (UC Berkeley)][[File:Vernier Template v2 screenshot.jpg|alt=screenshot of vernier_template.gds CAD file|none|thumb|200x200px|Vernier Template schematic.]] |
|||
*[[Resolution Test structures]] - '''''To Be Added''''' |
|||
*Contact Alignment Marks: |
|||
*#[https://www.cnfusers.cornell.edu/contact_litho_alignment_keys#:~:text=Standard%20Contact%20Alignment%20Mark CNF Contact Marks] - designed by the Cornell Nanoscale Science & Technology Facility staff. |
|||
*#*"''Polygons are Clear''" polarity, so 2nd layer has transparent region around alignment mark. |
|||
*#Male/female alignment marks with vernier (step=0.5um): [[Media:Contact-AlignMarks Vernier DemisDJohn v4.oas|OASIS]] / [[Media:Contact-AlignMarks Vernier DemisDJohn v4.gds|GDS]] format (Designed by [[Demis D. John]]) |
|||
*#*2nd layer has cells with both polarities (positive and negative, with window for viewing during alignment) |
|||
:::{| |
|||
|[[File:Contact-AlignMarks Vernier DemisDJohn v3 Screenshot.png.png|alt=screenshot of Contact-AlignMarks_Vernier_DemisDJohn_v3.oas|none|thumb|200x200px|Alignment Mark with Vernier]] |
|||
|[[File:Inverted Contact-AlignMarks with Vernier.png|alt=screenshot of inverted alignment mark|none|thumb|214.2x214.2px|Inverted 2nd layer, for transparent region around Alignment Marks (easier coarse alignment)]] |
|||
|} |
|||
====GCA Stepper==== |
|||
* [[Stepper Mask-Making Guidelines (Generic)]] |
|||
*[[:File:GCA Stepper MaskPlate Master-DarkField 5x.gds|GCA Photomask Template]]: Dark-field (polygons/objects are clear) at 5x Magnification (GDS) |
|||
**''This template is designed to be submitted to the photomask vendor to print as-is, no scaling applied.'' |
|||
**''Insert your designs into the template as Instances scaled UP by 5x.'' |
|||
**''During exposure, set the blades to 90/90 to block out AutoStep200 DFAS openings'' |
|||
*[[Media:GCA Global Mark.gds|GCA Global Alignment Mark CAD File (GDS)]] |
|||
*[[:File:GCA Local Alignment Mark.gds|GCA Local Alignment Mark (GDS)]] |
|||
*[[:File:GCA Local Alignment Mark Dotted.gds|GCA Local Alignment Mark Dotted (GDS)]] - helps for low-contrast topography |
|||
====ASML Stepper==== |
|||
* [[Stepper Mask-Making Guidelines (Generic)]] |
|||
* [https://docs.google.com/document/d/1b9YT11RPsl-UlLvN74hrQvG01OcYDL16r6I5lPOlBEo/edit?usp=sharing ASML-specific Mask Making Guidelines] - ''Access is restricted to trained users only.'' |
|||
*[[Calculators + Utilities#Example%20CAD%20File|Example Reticle/Mask CAD File]], designed in [[Calculators + Utilities#KLayout|KLayout]]. |
|||
====Heidelberg MLA150==== |
|||
*[[MLA150 - CAD Files and Templates]] |
|||
====Other sources of lithography CAD files==== |
|||
*[https://www.mems-exchange.org/users/litho-templates/ MEMS Exchange] - has some useful alignment markers, registration/alignment verniers etc. |
|||
*[https://www.epfl.ch/research/facilities/cmi/process/photolithography/layout-design/ EPFL CMi] - CMi layout template has some useful guidelines and resolution test structures. |
|||
==General Calculators== |
|||
*[https://www.anaconda.com/download/ Anaconda Python] |
*[https://www.anaconda.com/download/ Anaconda Python] |
||
| Line 119: | Line 186: | ||
**A versatile online interpreter/calculator, allowing calculations such as "Volume of 1.5g of Silicon", "melting point of SiO2" or "520°C in Fahrenheit". |
**A versatile online interpreter/calculator, allowing calculations such as "Volume of 1.5g of Silicon", "melting point of SiO2" or "520°C in Fahrenheit". |
||
==Python Scripts== |
|||
''These scripts are best run in the [https://pythonhosted.org/spyder/installation.html Spyder IDE], which is easily installed via [https://www.anaconda.com/download/ Anaconda], [http://python-xy.github.io Python(X,Y)] |
''These scripts are best run in the [https://pythonhosted.org/spyder/installation.html Spyder IDE], which is easily installed via [https://www.anaconda.com/download/ Anaconda], [http://python-xy.github.io Python(X,Y)].'' |
||
'''If you use/modify these scripts in a publication, <u>please consider citing the author(s)</u>.''' See our [[Frequently Asked Questions#Authorship on Publications|publication policy]] for more info. |
|||
====[https://github.com/demisjohn/Keithley-I-V-Sweep Keithley I-V Sweep]==== |
|||
*Sweep voltage and plot current vs. voltage using a Keithley SMU. |
|||
*Already installed at the Probe Station in Bay 4, and on the QFI Thermal Microscope (Use '''''Spyder (Anaconda Python)''''' to run). |
|||
*Requires the [https://pyvisa.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ pyvisa] python module. |
|||
====[https://github.com/demisjohn/QFI-Scope-Thermal-Analysis QFIScope Thermal Analysis (Demis D. John)]==== |
|||
*Import 2D temperature data from the [[IR Thermal Microscope (QFI)]] and plot temperature profiles at user-specified locations. |
|||
*Already installed on the QFI Infrared Microscope. |
|||
====[[Laser Etch Monitor Simulation in Python|Laser Etch Monitor Simulation in Python (Demis D. John)]]==== |
|||
*Simulate your laser endpoint signal as you dry-etch through a stack of thin-film layers, using an open-source electromagnetics module. |
|||
====[https://github.com/lbolla/EMpy/blob/master/examples/nk.py Optical Constants of Nanofab Films - nk.py (Demis D. John)]==== |
|||
*Python functions for returning '''''n''''' (refractive index) & '''''k''''' (extinction coefficient) of various NanoFab thin-films at a specified wavelength (aka. optical dispersion models) |
|||
*[https://github.com/demisjohn/Keithley-I-V-Sweep Keithley I-V Sweep] |
|||
**Sweep voltage and plot current vs. voltage using a Keithley SMU. |
|||
**Already installed at the Probe Station in Bay 4, and on the QFI Thermal Microscope (Use '''''Python(X,Y)''''' to run). |
|||
**Requires the [https://pyvisa.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ pyvisa] python module. |
|||
*[https://github.com/demisjohn/QFI-Scope-Thermal-Analysis QFIScope Thermal Analysis] |
|||
**Import 2D temperature data from the [[IR Thermal Microscope (QFI)]] and plot temperature profiles at user-specified locations. |
|||
**Already installed on the QFI Infrared Microscope. |
|||
*[[Laser Etch Monitor Simulation in Python|Laser Etch Monitor Simulation in Python]] |
|||
**Simulate your laser endpoint signal as you dry-etch through a stack of thin-film layers, using an open-source electromagnetics module. |
|||
*[https://github.com/lbolla/EMpy/blob/master/examples/nk.py nk.py (Demis D. John)] |
|||
**''Python functions for returning'' '''n''' ''(ref. idx.) &'' '''k''' ''(ext. coeff.) of various NanoFab thin-films at a specified wavelength (aka. dispersion models).'' |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:15, 3 October 2024
This page lists a few online calculators and utilities that are useful to lab users.
Fabrication Processes & Converters
- Thermal Oxide Calculator (BYU)
- Thermal Oxide Calculator (Leland Stanford Jr.)
- This Thermal Ox calculator allows you to tweak the calculation using the Partial Pressure variable, to match your experimental data.
- Conversion of Pressure Units (calculatoredge.com)
- Mean Free Path tables (Pfeiffer Vacuum)
- LelandStanfordJunior.com: Film Stress, Ion Implant, Thermal Oxidation, KOH Etching & online curve-fitting
Material Parameters
- WebElements: Compounds
- Boiling points of various compounds can tell you how volatile an etch product may be in a reactive ion etch, or whether they need to be wet-etched instead.
- Physical Properties of Semiconductors (Ioffe Institute)
- Kurt J Lesker: Material Deposition Chart
- Useful info about evaporating and sputtering many materials
- Kurt J. Lesker: Sputter Rates
- Sputter rates of various materials, indicative or hardness and dry etching properties.
Wet Etching
- Transene Inc. Chemical Compatibility Chart
- This table shows common metals and which Transene etchants they are attacked by/impervious to.
- A.R. Clawson, "Guide to references on III±V semiconductor chemical etching", 2001
- Enormous review of published wet etches of many semiconductors and alloys. The only thing it's missing is a hyperlinked table of contents.
Refractive Indices
Optical constants of many common materials. Useful for Optical thin-film analysis (ellipsometry/spectroscopic fitting), laser etch monitoring, optical filter/mirror/anti-reflection coating design, photonic devices etc.
Scripts + Programs
Analysis Programs
- AmScope Software - microscope image analysis software
- AmScope Calibration File containing calibrations for all NanoFab microscopes: Download Here
- Also available on Nanofiles-SFTP / Manuals / Amscope
- FIJI - scientific image anaylsis software
- The Microscope Measurement Tools plugin has pre-configured calibrations for NanoFab microscopes & SEMs, and allows you to draw length measurements.
- Calibrations in this plugin repository are out of date as of microscope upgrades in 2019.
- There are many other useful plugins, for particle counting, creating animations etc.
- The Microscope Measurement Tools plugin has pre-configured calibrations for NanoFab microscopes & SEMs, and allows you to draw length measurements.
- Gwyddion - free analysis software for Atomic Force Microscopes (AFMs) and other 3D data.
- Sophisticated leveling, slicing, roughness/particulate analysis functions etc.
- Can open Bruker NanoScope files, from the AFM
- ProfilmOnline.com (Filmetrics) - online analysis/storage/sharing of 3D topographical data and images.
- You can share an interactive 3D render of your AFM or Profilm3D scans with this tool.
- Example AFM Scan, taken with NanoFab equipment, shared online for interactive analysis (slice, flatten etc.).
CAD Layout and Mask Design
CAD Layout Programs
Use these for designing your lithography mask plates.
L-Edit
Powerful multi-layer layout program. Sophisticated object instantiation and array layout, to reduce files sizes and easily push changes to multiple cells.
- UCSB's ECE dept. provides an academic license for this software (no industrial users!), email help@ece.ucsb.edu to obtain the software.
- Windows only.
- See this L-Edit Tutorial for a good starter guide. Written by Cherry Gupta, courtesy of Prof. Sumita Pennathur.
KLayout
A free, open-source, and fast/simple CAD tool for mask/reticle layout. Also has powerful functions, DRC, scriptiable and can handle very large files (GB's) efficiently.
Download at klayout.de.
- Available on Windows, Mac or *Nix.
- Fast viewing of layer overlay, overlay multiple files, cell hierarchy, large (>1GB) files etc.
- Supports the same core functionality as L-Edit - hierarchical Cell Instances, arrays, programmable Cells (PCells) etc.
- Easily scriptable with Python or Ruby, with decent tutorials.
- KLayout Design Tips: important info on making "valid" CAD files, and setting up the program for efficient use.
- Univ. of Waterloo QNFCF has produced some good video tutorials on KLayout, here.
LayoutEditor
- Free editor for GDS, OASIS, DXF etc. available on Windows, MacOS, Linux.
- Scriptable with Python, Ruby, C++
AutoCAD
Many photomask vendors can accept AutoCAD DWG files, but these can only be opened in AutoCAD (not KLayout or other layout programs). Although AutoCAD can produce a cross-compatible DXF file, we see many design/conversion issues with these files. This is because many shapes and line-types (Curves and Line/polyline/LWLine for example) used in AutoCAD don't convert as expected into the polygons needed for printing. Also the DXF file format itself often creates problems, such as incorrect scaling or badly-filled/unclosed polygons.
CAD Design Tips
Cells and Instancing
All major chip layout programs support "Cells" and similar structures for hierarchical layout. It is highly recommended that you understand and use the concept of "Cells" in your design. This circumvents many problems with enormous file sizes (due to huge numbers of identical polygons), and if used properly, helps tremendously with programming the Stepper lithography machines. Links to documentation below:
- Create a new cell, and instancing that cell: KLayout Docs : Creating a Cell instance
- Viewing only some levels of the heirachy, to prevent drawing all objects: KLayout Docs: Viewing Cell Heirarchy
File Types
OASIS files tend to be much smaller than GDS files, and they also save the Layer Names (not just number). Alternatively, in KLayout the function File > Save Session will save the entire view including layer styles and window/zoom locations will be saved. You can share this file, as the entire design file is embedded within it, but it may not be as robust between KLayout versions.
DXF Files can often cause problems because the format varies widely depending on the program they are exported from. For example, DXF can lose the "scaling" causing polygons to be 1000x larger than expected, or unexpectedly cause some shares to get filled in.
KLayout Design Tips
See the above page for important info on making "valid" CAD files, and setting up KLayout for efficient use.
Handling very large files
If you will be generating millions of identical shapes (eg. repeating array of circles), the file size can quickly become enormous due to all the stored polygon points. You can reduce the number of polygon points stored by:
- Reduce the number of points in each shape/circle if possible.
- Use Cell instancing so that only one, or a few, polygons are defined, and that same polygon is then only referenced as a repeating Cell instance. (See above for tutorials).
- The OAS file type generates much smaller files, and most photomask vendors can accept this. Photomask vendors are used to handling large files.
- Photomask vendors are able to take multiple files and insert them into the final reticle – you just need to provide a clear schematic showing the exact insertion coordinates for each file (with respect to the origin of each file). They can also do some boolean operations (for a fee).
Example CAD File
Here is an example CAD file, showing the use of Layers and Cells, designed in KLayout. The device is fictional, for illustrative purposes only.
- CAD_Tutorial_for_Reticle_v1.OAS , or GDS version (Demis D. John)
- Cell "Device_Layout" shows a single device, with each Layer overlaid as it would be in a fabricated device. Each Layer (eg. a "process step" such as Mesa etch, Pad Metal etc.) is placed into it's own Cell.
- Every Cell's Origin (0,0) lies on top of one another in the final Device_Layout.
- One way this can be accomplished is by selecting the objects/polygons you want to make into a new Cell, then use the function Edit > Selection > Make Cell, and uncheck the "Put Origin at..." checkbox, so the new Cell maintains the same origin as the original view.
- The Cell "Reticle_Layout" can be exported by itself (right-click the Cell name), for sending to the photomask manufacturer.
- Here is an example GDS file (download) for submission to the photomask manufacturer, with all objects moved to a single Layer.
- See the Stepper Mask Making Guidelines page for an example of how to program this Reticle into an ASML Stepper job.
CAD Files & Templates
General CAD files for Lithography
- Vented Font (GDS) - a font good for liftoff (no enclosed holes). (Designed by Demis D. John)
- See this comment for instructions on installing the font into KLayout.
- Alignment/Registration Vernier Scales (GDS) - used to measure the misalignment between different layers (step=0.1um). (Designed by Demis D. John)
- Resolution Test structures - To Be Added
- Contact Alignment Marks:
- CNF Contact Marks - designed by the Cornell Nanoscale Science & Technology Facility staff.
- "Polygons are Clear" polarity, so 2nd layer has transparent region around alignment mark.
- Male/female alignment marks with vernier (step=0.5um): OASIS / GDS format (Designed by Demis D. John)
- 2nd layer has cells with both polarities (positive and negative, with window for viewing during alignment)
- CNF Contact Marks - designed by the Cornell Nanoscale Science & Technology Facility staff.
GCA Stepper
- GCA Photomask Template: Dark-field (polygons/objects are clear) at 5x Magnification (GDS)
- This template is designed to be submitted to the photomask vendor to print as-is, no scaling applied.
- Insert your designs into the template as Instances scaled UP by 5x.
- During exposure, set the blades to 90/90 to block out AutoStep200 DFAS openings
- GCA Global Alignment Mark CAD File (GDS)
- GCA Local Alignment Mark (GDS)
- GCA Local Alignment Mark Dotted (GDS) - helps for low-contrast topography
ASML Stepper
- Stepper Mask-Making Guidelines (Generic)
- ASML-specific Mask Making Guidelines - Access is restricted to trained users only.
- Example Reticle/Mask CAD File, designed in KLayout.
Heidelberg MLA150
Other sources of lithography CAD files
- MEMS Exchange - has some useful alignment markers, registration/alignment verniers etc.
- EPFL CMi - CMi layout template has some useful guidelines and resolution test structures.
General Calculators
- Anaconda Python
- A free Matlab-like IDE and GUI, using the Python language. The Spyder interface is modeled after Matlab.
- Includes the scientific Python libraries needed for array math (numpy), plotting (matplotlib), data science (pandas) and many others. Many open-source packages are available to extend capabilities. The PyVisa module adds equipment control capabilities for automated measurements.
- Octave Online Interpreter (online-utility.org)
- A Matlab-like command-line interface, powered by Python Octave.
- Wolfram Alpha
- A versatile online interpreter/calculator, allowing calculations such as "Volume of 1.5g of Silicon", "melting point of SiO2" or "520°C in Fahrenheit".
Python Scripts
These scripts are best run in the Spyder IDE, which is easily installed via Anaconda, Python(X,Y).
If you use/modify these scripts in a publication, please consider citing the author(s). See our publication policy for more info.
Keithley I-V Sweep
- Sweep voltage and plot current vs. voltage using a Keithley SMU.
- Already installed at the Probe Station in Bay 4, and on the QFI Thermal Microscope (Use Spyder (Anaconda Python) to run).
- Requires the pyvisa python module.
QFIScope Thermal Analysis (Demis D. John)
- Import 2D temperature data from the IR Thermal Microscope (QFI) and plot temperature profiles at user-specified locations.
- Already installed on the QFI Infrared Microscope.
Laser Etch Monitor Simulation in Python (Demis D. John)
- Simulate your laser endpoint signal as you dry-etch through a stack of thin-film layers, using an open-source electromagnetics module.
Optical Constants of Nanofab Films - nk.py (Demis D. John)
- Python functions for returning n (refractive index) & k (extinction coefficient) of various NanoFab thin-films at a specified wavelength (aka. optical dispersion models)