Surface Analysis (KLA/Tencor Surfscan): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
reorg, remove old SOP, replaced with new PDF SOP's for each wafer size |
→Documentation: added info, and inof on LPC wafers |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
==About== |
==About== |
||
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface. |
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface. |
||
It can scan wafers in size from 4 to 8 inches. Piece-parts are more difficult but can be scanned with a custom recipe. |
|||
4-inch wafers are the most standard size to measure. |
|||
For measuring very low particle counts accurately, purchase "low particle count" (LPC) wafers from a Silicon wafer vendor, and keep the wafers in the case and clean at all times until use. |
|||
==Documentation== |
==Documentation== |
||
=== |
===Operating Procedures=== |
||
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/0/04/SURFSCAN_6200_8inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 8inch wafers] * |
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/0/04/SURFSCAN_6200_8inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 8inch wafers] * |
||
| Line 22: | Line 28: | ||
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/8/87/SURFSCAN_6200_4inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 4inch wafers] * |
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/8/87/SURFSCAN_6200_4inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 4inch wafers] * |
||
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/1/1a/SURFSCAN_6200_2_and_3inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 2 and 3inch wafers] * |
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/1/1a/SURFSCAN_6200_2_and_3inch_wafers.pdf Surfscan 6200 2 and 3inch wafers] * |
||
**''You must provide your own 2/3-inch Cassette.'' |
|||
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/4/4e/SURFSCAN_6200_Small_substrates.pdf Surfscan 6200 Small samples] * |
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/4/4e/SURFSCAN_6200_Small_substrates.pdf Surfscan 6200 Small samples] * |
||
**''You must water-mount your pieces to a 4-inch wafer.'' |
|||
*[[Wafer scanning process traveler]] |
*[[Wafer scanning process traveler|Wafer Particle Count - Process Traveler]] |
||
**''This is the procedure Staff uses to calibrate particle counts on our deposition tools.'' |
**''This is the procedure Staff uses to calibrate particle counts on our deposition tools.'' |
||
=== |
===Other Documentation=== |
||
* |
*[https://wiki.nanotech.ucsb.edu/w/images/9/96/Surfscan-Operation-Manual.pdf Operations Manual] |
||
**''For detailed measurement info, it is highly recommended that you read the manual.'' |
**''For detailed measurement info, it is highly recommended that you read the manual.'' |
||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
==Examples== |
==Examples== |
||
<br /> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
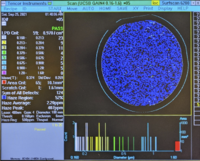
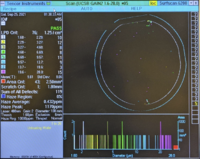
|+A low-particle 4-inch wafer example: |
|+A low-particle 4-inch wafer example: |
||
Revision as of 18:43, 4 January 2024
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
About
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface.
It can scan wafers in size from 4 to 8 inches. Piece-parts are more difficult but can be scanned with a custom recipe.
4-inch wafers are the most standard size to measure.
For measuring very low particle counts accurately, purchase "low particle count" (LPC) wafers from a Silicon wafer vendor, and keep the wafers in the case and clean at all times until use.
Documentation
Operating Procedures
- Surfscan 6200 8inch wafers *
- Surfscan 6200 6inch wafers *
- Surfscan 6200 4inch wafers *
- Surfscan 6200 2 and 3inch wafers *
- You must provide your own 2/3-inch Cassette.
- Surfscan 6200 Small samples *
- You must water-mount your pieces to a 4-inch wafer.
- Wafer Particle Count - Process Traveler
- This is the procedure Staff uses to calibrate particle counts on our deposition tools.
Other Documentation
- Operations Manual
- For detailed measurement info, it is highly recommended that you read the manual.
Examples
| Gain 4: Small Particles
(0.160µm – 1.60µm) |
Gain 2: Large Particles
(1.60µm – 28.0µm) |
|---|---|
|
|
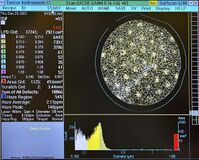
| Gain 4: Small Particles
(0.160µm – 1.60µm) |
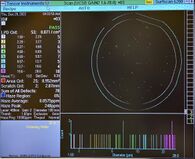
Gain 2: Large Particles
(1.60µm – 28.0µm) |
|---|---|
|
|
