Surface Analysis (KLA/Tencor Surfscan): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
|||
| (83 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|location=Bay 5 |
|location=Bay 5 |
||
|description = Surface Analysis |
|description = Surface Analysis |
||
|manufacturer = KLA/Tencor |
|||
|manufacturer = Tencor |
|||
|materials = |
|materials = |
||
|toolid= |
|toolid= |
||
}} |
}} |
||
==About== |
==About== |
||
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface. |
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface. |
||
It can scan wafers in size from 4 to 8 inches. Piece-parts are more difficult but can be scanned with a custom recipe. |
|||
4-inch wafers are the most standard size to measure. |
|||
For measuring very low particle counts accurately, purchase "low particle count" (LPC) wafers from a Silicon wafer vendor, and keep the wafers in the case and clean at all times until use. |
|||
==Documentation== |
==Documentation== |
||
===Operating Procedures=== |
|||
*[[KLA-Tencor Surfscan - Standard Operating Procedure|Standard Operating Procedure]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[Errors]] |
|||
*[https://wiki.nanofab.ucsb.edu/w/images/2/29/Wafer_Particle_Count-Process_Traveler.pdf Wafer Scanning Instructions] |
|||
==Standard Recipes== |
|||
**''This is the procedure Staff uses to calibrate particle counts on our deposition tools. After the scan is complete you need to press ENTER on a small laptop. The Data will be saved on: Desktop/Local Disk(C)/Users/Public/Public Documentation] The data will be saved as a photo.'' |
|||
*[[Surfscan SOP for small substrates]] (''You must water-mount your small sample or wafer (2inch or 3 inch) to a carrier wafer)'' |
|||
*[[Surfscan SOP for 4inch wafers]] |
|||
Recipes |
|||
*[[Surfscan SOP for 6inch wafers]] |
|||
<br /> |
|||
*[[Surfscan SOP for 8inch wafers]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
**'' Very detailed instructions |
|||
===Other Documentation=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[Surfscan Errors and Workarounds|Common Errors & Workarounds]] |
|||
<br /> |
|||
==Examples== |
==Examples== |
||
<br /> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|+A low-particle 4-inch wafer example: |
|+A low-particle 4-inch wafer example: |
||
Latest revision as of 23:04, 20 November 2024
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
About
This system uses a laser-based scattering method to count size and distribution of particles (or other scattering defects) on a flat wafer surface.
It can scan wafers in size from 4 to 8 inches. Piece-parts are more difficult but can be scanned with a custom recipe.
4-inch wafers are the most standard size to measure.
For measuring very low particle counts accurately, purchase "low particle count" (LPC) wafers from a Silicon wafer vendor, and keep the wafers in the case and clean at all times until use.
Documentation
Operating Procedures
- Wafer Scanning Instructions
- This is the procedure Staff uses to calibrate particle counts on our deposition tools. After the scan is complete you need to press ENTER on a small laptop. The Data will be saved on: Desktop/Local Disk(C)/Users/Public/Public Documentation] The data will be saved as a photo.
- Surfscan SOP for small substrates (You must water-mount your small sample or wafer (2inch or 3 inch) to a carrier wafer)
- Wafer Particle Count - Process Traveler
- Very detailed instructions
Other Documentation
- Operations Manual
- For detailed measurement info, it is highly recommended that you read the manual.
Examples
| Gain 4: Small Particles
(0.160µm – 1.60µm) |
Gain 2: Large Particles
(1.60µm – 28.0µm) |
|---|---|
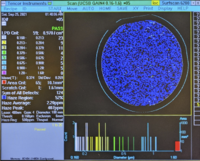
|
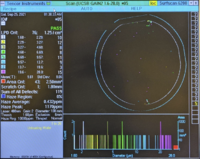
|
| Gain 4: Small Particles
(0.160µm – 1.60µm) |
Gain 2: Large Particles
(1.60µm – 28.0µm) |
|---|---|
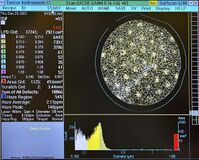
|
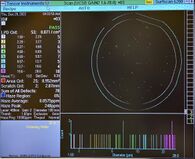
|
