Suss Aligners (SUSS MJB-3): Difference between revisions
→Backside Alignment: added MJB-IR alignment example image. |
updated IR image |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
====Backside Alignment==== |
====Backside Alignment==== |
||
[[File:MJB-IR - squares alignment and field of view.png|alt=IR image of two front-to-back aligned squares|thumb|140x140px|Example of the Infrared image showing front-to-back alignment of squares on either side of the wafer. Design your alignment marks according to this field of view 2025-11-19. (Credit: [[Demis D. John]])]] |
|||
On the Standard MJB-3, special black chucks may be used for optically transparent materials, allowing you to view through the wafer. |
On the Standard MJB-3, special black chucks may be used for optically transparent materials, allowing you to view through the wafer. |
||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
*Infrared camera and computer for imaging. |
*Infrared camera and computer for imaging. |
||
*Through-wafer alignment and/or inspection. |
*Through-wafer alignment and/or inspection. |
||
*Design your alignment marks according to this field of view: |
|||
[[File:IR Alignment check 01 - crop.png|alt=Screenshto of IR camera showing front-to-back alignment|none|thumb|MJB-IR front-to-back alignment check through Silicon substrate, with |
[[File:IR Alignment check 01 - crop.png|alt=Screenshto of IR camera showing front-to-back alignment|none|thumb|MJB-IR front-to-back alignment check through Silicon substrate, with one square on the front, aligned to few-mm photoresist pattern on the backside. 2025-11-19. (Credit: [[Demis D. John]])]] |
||
<br /> |
<br /> |
||
===Exposure Optical Spectrum with No Filter=== |
===Exposure Optical Spectrum with No Filter=== |
||
Revision as of 02:56, 20 November 2025
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
About
We have two high-performance mask aligners for contact exposure processes. They are manual mechanical systems alignment, contact/proximity, with exposure shuttered by a timer. The resolution (depending on contact mode, optics and exposure wavelength and "operator technique") is into the submicron region. (See descriptions for our "Std." and "IR" units).
Our units are configured for the near-UV window (365 and 405 nm). All units have the "vacuum contact" option extending resolution to ~0.7 microns. Higher resolution optic systems that can be supplied by Suss are given below. The standard soft and hard contact modes of mechanical and pneumatic pressure respectively, give resolution to ~1 micron.
Exposures can be done on substrates from small "piece parts" of less than 1 cm square to substrates of 3 inch diameter or square. Masks up to 4 inches in size can be used although only 3” x 3” of this area is usable. A 4” wafer can be exposed with the system. However, only 3” x 3” will be exposed on the wafer and vacuum mode is unavailable.
Backside Alignment
On the Standard MJB-3, special black chucks may be used for optically transparent materials, allowing you to view through the wafer.
For backside alignment through opaque materials such as Si or GaAs, our IR aligner has backside infrared illumination (halogen bulb) through these black chucks. An IR camera is installed to view the infrared image.
Using a filter, the IR system can be configured for I-line (350 nm) only, assisting in resolution.
Detailed Specifications
- Wafer size: 3" max. for vacuum mode; 4” for soft contact (3” x 3” exposure area)
- Substrate size: 3" x 3" max.
- Wafer / substrate thickness: 0-4.5 mm
- Mask plate size: 4" x 4" x 0.090", typically soda-lime glass. Smaller (eg. 3") is also acceptable.
- Exposure optics:
- Standard unit (Aligner #1): 350-450 nm/200 W mercury lamp
- IR unit: 280-450 nm/200 W mercury lamp (can filter to 350 nm)
- Additional manufacturer options (none installed on our systems):
- DUV (polychromatic): 240-260 nm/350 W Cd-Xe lamp; 0.2 micron resolution (PMMA)
- DUV (monochromatic): 248 nm/KrF excimer laser; 0.3 micron resolution (PMMA)
- 193 nm/ArF excimer laser; 0.2 micron resolution (PMMA)
- Uniformity:
- ±3% over 2" diameter
- ±5% over 3" diameter
- Min. Feature Size:
- Approx.
IR Aligner
- Backside illumination with halogen bulb & transparent chuck
- Infrared camera and computer for imaging.
- Through-wafer alignment and/or inspection.
- Design your alignment marks according to this field of view:

Exposure Optical Spectrum with No Filter
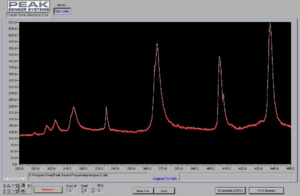
Exposure Optical Spectrum with Filter for i-line Exposure
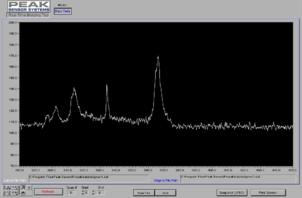
Documentation
Mask Plate Info
- Mask Making Guidelines - Contact Masks - in progress
- Photomask Ordering Procedure for UCSB Users - see this page for how to submit your order into the purchasing system.
CAD Files
For designing your mask plates.
- Male/female alignment marks (GDS): MA6-FrontBack_AlignMarks_only.gds
- CAD Layout Programs
- CAD Design Tips
- CAD Files & Templates - alignment markers, verniers and other useful CAD objects
Recipes
- Recipes > Lithography > Photolithography Recipes > SUSS MJB-3
- Starting recipes for various I-Line photoresists, positive and negative.
- Photolithography - Manual Edge-Bead Removal Techniques
- Edge bead removal helps improve resolution and alignment quality.
